CyberKnife for Cancer Treatment
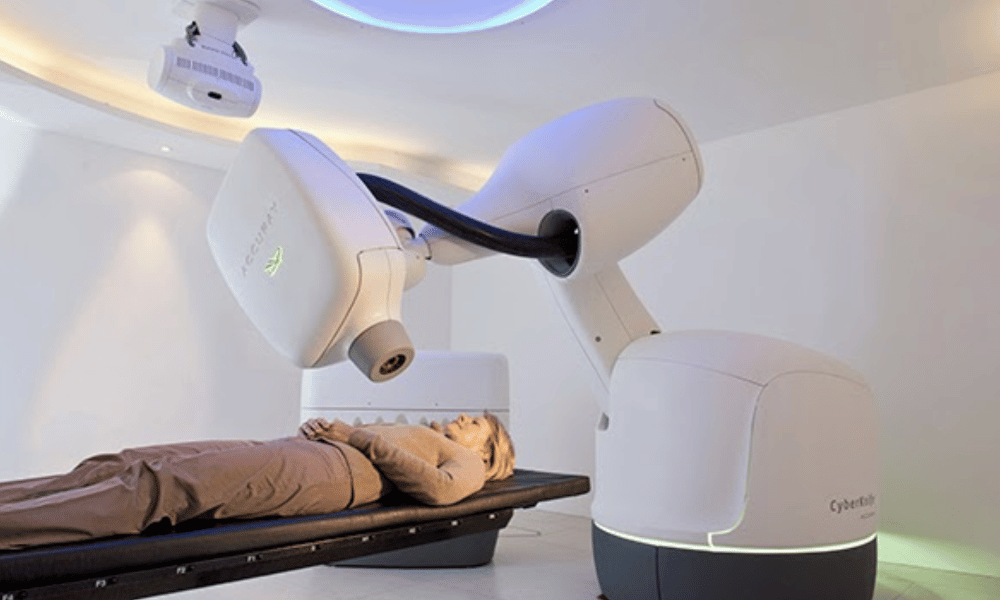
CyberKnife is a non-invasive, robotic radiosurgery system that uses advanced imaging and a robotic linear accelerator to deliver highly focused radiation with sub-millimeter precision directly to tumors. This precision lets clinicians deliver a high therapeutic dose to the tumor while minimizing exposure to nearby healthy tissue, often reducing the number of treatment sessions compared with conventional radiation therapy.
Considering CyberKnife for Cancer Treatment? Your Guide to Precision Radiotherapy
A cancer diagnosis raises many questions about treatment options. CyberKnife treatment offers a non‑surgical alternative that combines robotics and image‑guided radiosurgery to target tumors with exceptional accuracy. Depending on the indication, treatments are typically delivered in 1–5 outpatient sessions (fractions), though the exact plan depends on tumor type and location.
Technically, CyberKnife is used for stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) in the brain and stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for body sites. The system’s real‑time imaging and motion tracking enable radiation to follow tumor movement (for example, with breathing), improving precision and reducing dose to surrounding organs. For many patients this means fewer side effects and a shorter recovery period than traditional surgery or extended radiation courses.
If you’re exploring options, this guide explains how CyberKnife works, which cancers it commonly treats, who may be a candidate, and what to expect from recovery and travel for treatment. To get a personalized assessment and cost estimate, consider requesting a consultation with an experienced team familiar with CyberKnife technology.
What Types of Cancer Can CyberKnife Treat?
CyberKnife is most effective for many solid tumors that are small to medium in size or located in sensitive, hard-to-reach areas of the body. Common indications include tumors in the brain, lung, prostate, spine, liver and pancreas, as well as selected recurrent lesions.
The system’s precision and motion‑tracking make it a versatile option across the body. Below are the primary tumor types and brief notes on when CyberKnife is typically considered:
- Brain Tumors: Primary and metastatic brain tumors, acoustic neuromas, meningiomas, and pituitary adenomas — often chosen when preserving neurological function is critical; typically delivered as SRS.
- Lung Cancer: Small primary lung tumors and lung metastases. CyberKnife’s real‑time tracking compensates for breathing motion, making it useful for solitary lesions or patients who cannot have surgery.
- Prostate Cancer: An option for early-stage prostate cancer and some local recurrences; typically completed in 1–5 high‑dose fractions as a non-surgical alternative to extended conventional radiation courses.
- Spinal Tumors: Both primary and metastatic spinal tumors where precision is needed to protect the spinal cord and nerve roots; commonly used when surgery is high‑risk.
- Liver Tumors: Primary liver cancers and liver metastases — selected small lesions can be treated with SBRT approaches.
- Pancreatic Cancer: For some challenging pancreatic tumors, CyberKnife can be used alone or in combination with other therapies, typically for localized disease or palliation.
- Kidney Cancer: Certain small renal lesions can be suitable for radiosurgery when surgery is not feasible.
- Recurrent Cancers: Selected recurrent tumors may be re-treated locally with CyberKnife while minimizing dose to previously irradiated healthy tissue.
- Trigeminal Neuralgia: Although not a cancer, CyberKnife is also an established radiosurgical option for trigeminal neuralgia when surgery is not desired.
Patients researching specific applications often search phrases like “CyberKnife for brain tumor,” “CyberKnife for prostate,” or “CyberKnife for lung.” For detailed eligibility and tumor‑specific protocols, see the eligibility section and the technical “How it works” explanation elsewhere on this page.
What Are the Symptoms and Causes of Cancers Treated by CyberKnife?
Symptoms of cancers treated with CyberKnife depend on the tumor’s location—headaches for some brain tumors, persistent cough for lung lesions, or abdominal pain for liver and pancreatic tumors. Causes are multifactorial and include genetics, lifestyle, infections, and environmental exposures.
Because CyberKnife is a treatment delivered to a variety of tumor types throughout the body, the warning signs and underlying causes vary widely. This section offers a concise, practical overview and next steps if you notice concerning symptoms.
Common Cancer Symptoms
Symptoms often reflect the tumor’s size and location. Watch for persistent or unexplained changes including:
- Unexplained weight loss: Significant, unintentional loss of weight.
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness not relieved by rest.
- Pain: Ongoing localized pain (e.g., back pain for spinal tumors, headaches for brain tumors, abdominal pain for liver/pancreatic tumors).
- Persistent cough or hoarseness: Particularly relevant for lung or throat cancers.
- Changes in bowel or bladder habits: Blood in stool or urine, or new difficulty urinating (may signal prostate or colorectal issues).
- Lumps or thickening: New lumps in breast, testicle, lymph nodes, or other soft tissues.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
While causes differ by cancer type, several well-established risk factors increase the likelihood of developing tumors:
- Genetics: Inherited mutations (for example BRCA or Lynch syndrome) raise risk for certain cancers.
- Lifestyle factors: Smoking is a leading cause of lung and throat cancers; heavy alcohol use, obesity, and poor diet contribute to other cancer types.
- Environmental exposure: Prolonged contact with carcinogens (asbestos, certain chemicals) and air pollution can increase lung cancer risk; ionizing radiation exposure is also a recognized risk.
- Infections: Some viruses and bacteria (HPV, hepatitis B/C, H. pylori) are linked to specific cancers.
- Age: Risk for many cancers increases with age.
If you notice persistent or worrying symptoms, contact your healthcare provider for evaluation. Practical next steps often include primary care assessment, targeted imaging (CT, MRI), and referral to a specialist or multidisciplinary team to confirm diagnosis and discuss treatment options such as CyberKnife based on tumor type and patient factors. For more on who may be eligible, see the eligibility section and the technical “How it works” overview on this page.
How Does CyberKnife Therapy Work?
CyberKnife delivers high‑dose radiation via a robotic arm, using real‑time imaging and motion tracking to target tumors with sub‑millimeter precision. The system enables clinicians to concentrate dose on the tumor while sparing surrounding healthy tissue, and most courses are completed in 1–5 outpatient sessions depending on the indication.
CyberKnife combines stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) for cranial targets and stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for extracranial sites. Below is a clear, patient‑focused breakdown of how the treatment is planned and delivered.
- Imaging and planning: You’ll have high‑resolution imaging (CT, MRI, sometimes PET) so the team can map the tumor’s exact size, shape, and relationship to nearby organs. That imaging is used to create a personalized treatment plan and dose distribution.
- Robotic delivery and precision: A lightweight linear accelerator mounted on a multi‑axis robotic arm delivers many thin beams from dozens or hundreds of directions. The robot’s mobility allows highly conformal dose shaping around the tumor.
- Real‑time tracking and movement compensation: CyberKnife’s imaging and tracking software monitor tumor movement (for example, with breathing). The system automatically adjusts beam aim to follow the tumor’s motion so radiation consistently hits the target, reducing dose to healthy tissue.
- Multi‑directional, converging dose: Each individual beam is relatively low dose; where many beams converge on the tumor the cumulative dose is tumor‑ablative. This focused approach (sometimes described as “dose painting”) maximizes tumor control while limiting exposure to organs at risk.
- Outpatient experience: Treatment is non‑invasive. Patients lie on a couch, usually without general anesthesia. Sessions typically last 30–90 minutes depending on complexity. Most treatment courses are 1–5 fractions (sessions), though the exact number is set by the treating team.
What the patient feels: setup is comfortable, and staff verify positioning with imaging before each session; you should expect to lie still but can breathe normally in many cases. After treatment, routine follow‑up imaging assesses response over weeks to months. If you want a visual aid, consider adding a simple diagram showing imaging → planning → robotic delivery to clarify the workflow for readers.
Am I Eligible for CyberKnife Treatment?
Eligibility for CyberKnife depends on tumor size, location, type, prior treatments, and overall health. It is often an excellent option for small to medium tumors in sensitive locations or for patients who are not good candidates for surgery.
A multidisciplinary team—typically a radiation oncologist, medical oncologist, and surgeon—evaluates each case to determine whether CyberKnife is the best option. While versatile, CyberKnife is not appropriate for every tumor or patient. Key factors the team considers include:
- Tumor characteristics:
- Size: CyberKnife is most effective for small to medium tumors—many centers use it for lesions typically less than about 5–6 cm, though thresholds vary by site and clinical protocol.
- Location: Tumors in critical areas (brain, spine, or near major organs) that require high precision are often good candidates.
- Type: Solid tumors are commonly treated; response varies by histology and individual tumor biology.
- Previous treatments:
- CyberKnife can be a primary treatment or used for selected recurrences after surgery, conventional radiation, or chemotherapy.
- For patients who have already received substantial conventional radiation, carefully planned re‑irradiation with CyberKnife may be an option in localized areas.
- Overall health and practical considerations:
- Patients who are poor surgical candidates due to age or co‑morbidities may prefer this non‑invasive option.
- Ability to tolerate lying still during sessions and follow the care plan is evaluated.
- Patient preference: Some patients choose CyberKnife to avoid surgical risks, shorten recovery time, or preserve organ function when appropriate.
Checklist for your consultation: bring all recent scans (CT/MRI/PET), pathology reports, a list of prior treatments, and contact information for your local care team. Note when surgery remains the preferred option—examples include very large tumors that require resection for symptom control or when immediate removal is necessary to prevent neurological compromise. An experienced CyberKnife team will review your records and recommend the best treatment option for your diagnosis and goals.
What is the Recovery Time and What Can I Expect After CyberKnife?
Recovery after CyberKnife is generally quick with minimal downtime. Most patients resume normal activities soon after treatment, experiencing only mild, localized side effects that typically resolve in days to weeks.
Because CyberKnife treatments are non‑invasive and delivered as outpatient sessions, the impact on daily life is often far less than with surgery. Below is what patients commonly experience and a sample follow‑up timetable (confirm exact timing with your treating team).
- Immediate return to activities: Most patients can go home the same day and resume light work, walking, and daily routines almost immediately after a session. There are no surgical incisions or general anesthesia in most cases.
- Minimal downtime: Mild fatigue is the most commonly reported symptom and may last a few days. Serious downtime is uncommon compared with major surgery.
- Typical mild side effects by site:
- Brain: Headache, mild nausea, or localized swelling — usually temporary and managed with medication if needed.
- Lung: Mild cough, shortness of breath, or fatigue that typically resolves.
- Prostate: Temporary urinary frequency or urgency and mild rectal irritation in some patients.
- Follow‑up care and expected timeline: A common follow‑up schedule (verify with your clinic) is an initial visit and imaging at about 6–12 weeks after treatment, then scans at roughly 3–6 month intervals for the first year to monitor tumor response. Radiation effects and tumor shrinkage can occur gradually over weeks to months.
Practical tips: stay hydrated, maintain light activity as tolerated, and report new or worsening symptoms to your care team promptly. If you have concerns about recovery time or how sessions will fit into your schedule, discuss expected session lengths and total treatment time with your radiation oncology team — most sessions last approximately 30–90 minutes depending on complexity. Patient experience varies, so your team will tailor follow‑up and support to your needs.
What are the Risks and Side Effects of CyberKnife?
Because CyberKnife delivers highly focused radiation with sub‑millimeter precision, overall procedural risks are lower than many conventional approaches. Still, like any radiation therapy, side effects can occur and vary by treatment site and dose.
Most patients experience only mild, temporary symptoms. Serious complications are uncommon but possible — your treating team will explain the risks specific to your tumor and location.
Common and Mild Side Effects
These typically resolve within days to weeks:
- Fatigue: The most frequently reported symptom after radiation treatment.
- Skin irritation: Redness or mild sensitivity at the entry site, similar to a mild sunburn.
- Nausea or vomiting: More likely when treating lesions in the abdomen or certain brain areas.
- Headaches or localized swelling: Possible after brain treatments; usually managed with short courses of medication.
- Temporary hair loss: If the scalp receives radiation for brain targets.
Less Common or More Serious Risks (Rare)
Because of precise dose delivery, severe complications are infrequent but can occur, especially when critical structures are adjacent to the tumor:
- Nerve or neurological injury: Potential numbness, weakness, or pain when nerves are near the treatment field.
- Organ inflammation or damage: For example, pneumonitis after lung radiation or liver inflammation after liver treatments — risk depends on dose and tumor proximity to organs.
- Radiation necrosis or delayed tissue effects: In rare cases, healthy tissue can be injured and require additional management.
- Secondary cancers: A very small long‑term risk exists with any form of radiation therapy; highly focused SRS/SBRT aims to minimize this exposure.
How risks are reduced: careful treatment planning, dose constraints to nearby organs, and motion management (to limit unintended dose) are standard strategies. If swelling or inflammation occurs, clinicians may use steroids or supportive care to manage symptoms.
What to Ask Your Doctor
- What specific side effects should I expect given my tumor location and planned dose?
- Who should I contact for urgent symptoms after treatment?
- What mitigation strategies will you use (dose limits, steroids, follow‑up imaging)?
Your radiation team will review individualized risks and the expected radiation dose to nearby organs during consultation. Ask for published outcomes or local complication rates for your tumor type if available — informed patients make better decisions about treatment versus surgical alternatives.
CyberKnife Treatment Worldwide: Cost Comparison Table
Costs for CyberKnife treatment vary widely by country, clinic, the specific cancer being treated, and the number of sessions. Many patients find substantial savings through medical tourism without sacrificing access to modern technology and experienced teams.
Price is a major consideration for cancer patients exploring CyberKnife. Estimates below reflect typical per‑course ranges for 1–5 sessions (fractions) and are intended as a general guide only. Actual quotes depend on the tumor type, pre‑treatment diagnostics, planning, and whether follow‑up care is included.
Estimated CyberKnife Cost Comparison (Per Treatment Course, 1-5 sessions):
| CountryEstimated Cost Range (USD)Notes | ||
| United States | $30,000 – $100,000+ | Highest costs globally; varies by state, hospital, and included services. |
| United Kingdom | $20,000 – $50,000+ | Public (NHS) access differs from private pricing; private care can be costly. |
| Germany | $18,000 – $45,000 | High-quality facilities and experienced teams; pricing varies by clinic. |
| Turkey | $10,000 – $25,000 | Competitive pricing; many JCI‑accredited hospitals and experienced teams. |
| India | $8,000 – $20,000 | Very affordable options with recognized specialists; confirm accreditation and outcomes. |
| Mexico | $9,000 – $22,000 | Good proximity for North American patients; verify clinic experience and included services. |
| South Korea | $15,000 – $30,000 | Advanced technology and experienced teams; pricing competitive relative to Western Europe and the US. |
Methodology note: these are approximate ranges based on clinic reports and typical 1–5 fraction courses; they generally exclude travel, accommodation, visas, and some pre/post‑treatment services. Always request a personalized quote that itemizes what is covered.
If cost is a key concern, ask clinics for a detailed breakdown (treatment, planning, imaging, team consultations, and follow‑up). For tailored pricing and to compare options, request a personalized quote from the clinic or a vetted medical tourism facilitator.
Why Consider CyberKnife for Cancer Treatment Abroad?
Patients consider CyberKnife abroad to access experienced teams and advanced technology at lower cost, often with faster appointment availability and a more personalized care experience than they might find locally.
Traveling for treatment is a major decision. For many patients, the potential benefits of receiving CyberKnife therapy overseas—cost savings, access to specialized teams, and shorter waits—can outweigh travel logistics when clinics are carefully vetted.
- Cost savings: As shown in the cost table, CyberKnife treatment can be significantly cheaper in certain countries, making it an attractive option for patients without full insurance coverage.
- Access to advanced technology and expertise: Many international centers invest in the latest CyberKnife systems and have experienced radiation oncology teams who specialize in radiosurgery.
- Shorter waiting times: In some health systems, waiting lists for specialized radiation therapy can be long; going abroad may allow faster treatment start dates when timing is critical.
- Personalized care and convenience: International clinics often provide concierge services, translators, and coordinated logistics to simplify the patient journey and focus on individualized care.
- Privacy and a focused recovery environment: Some patients value the discretion and chance to recover away from home stresses.
Decision checklist — before choosing to travel, confirm clinic accreditation, ask about the treating team’s experience with your tumor type, request outcome data or patient references, and get a detailed, itemized quote covering treatment, planning, imaging, and follow‑up. If you need help comparing options, contact an experienced facilitator or the clinic’s international patient team to clarify timelines, costs, and what support they provide during your treatment experience.
Which Countries Offer the Best Value for CyberKnife Treatment?
For CyberKnife, several countries balance advanced technology, experienced clinical teams, and competitive pricing—making them common choices for patients considering treatment abroad.
When evaluating value for CyberKnife treatment, patients look for a combination of up‑to‑date cyberknife systems, physician experience with specific tumor types (for example prostate or lung), international accreditation, and transparent pricing. The following countries frequently offer a strong mix of these factors:
- Turkey: Competitive pricing and many JCI‑accredited hospitals; major centers in Istanbul and Ankara have experienced oncology teams and modern CyberKnife installations.
- India: Known for affordability and specialist experience, with top hospitals in Delhi, Mumbai, and Bangalore offering CyberKnife treatment and internationally accredited care.
- Mexico: Popular with North American patients due to proximity and good value; modern clinics in several cities deliver CyberKnife with experienced teams.
- South Korea: Offers advanced technology and efficient care pathways; costs may be higher than in Asia’s lowest‑cost markets but remain competitive compared with the US and Western Europe.
- Germany: For patients seeking European standards of clinical excellence and research‑driven care, Germany provides high‑quality CyberKnife centers with experienced teams—typically at higher cost than Asia or Latin America but lower than some US private options.
How to evaluate a hospital: verify international accreditation (JCI or equivalent), confirm the treating radiation oncologist’s experience with your tumor type, ask for published outcomes or local complication rates, and request an itemized quote that lists what is included (planning, imaging, team consultations, and follow‑up). For many prostate and lung patients, comparing team experience and outcome data is as important as price when choosing the best treatment option.
What to Expect When Traveling for CyberKnife?
Expect a streamlined process when traveling for CyberKnife: remote case review and virtual consultations, coordinated travel logistics (flights, visas, accommodation), clinic transfers, and on‑site support such as translators and dedicated patient coordinators.
Traveling abroad for treatment can be made far easier by working with an experienced facilitator or the clinic’s international patient team. Below is a typical, step‑by‑step flow and practical guidance on what to prepare and expect.
- Initial inquiry & medical records review: Share your scans, pathology, and treatment history so the team can assess suitability and recommend options. Good guidance at this stage speeds up planning.
- Virtual consultation: A teleconference with the radiation oncologist reviews your case, discusses potential outcomes, and answers questions—ask about expected success rates, side effects, and follow‑up.
- Quotation and treatment plan: The clinic provides a detailed plan showing the number of sessions, estimated time on site, and an itemized quote covering planning, imaging, treatment, and follow‑up. Clarify what is excluded (travel, accommodation, translator fees).
- Travel logistics: Expect help booking flights, arranging visas, and reserving recovery‑friendly accommodation. Practical timeline: allow 4–6 weeks for planning, though urgent cases can sometimes be expedited.
- On‑site support: A local representative typically meets you on arrival, coordinates transport, and provides translators for consultations and treatment visits.
- Pre‑treatment and treatment: Final imaging and simulation are done onsite before starting your 1–5 CyberKnife sessions. Sessions are outpatient; most patients can return to their accommodation the same day.
- Post‑treatment care & follow‑up: Clinics commonly offer remote follow‑up or detailed reports you can share with your local team. Confirm the follow‑up schedule and who will coordinate ongoing imaging.
Documents to prepare: recent CT/MRI/PET scans, pathology reports, lists of medications, prior treatment summaries, passport, and local physician contact details. Helpful questions for virtual consults: “What outcomes can I expect for my tumor type?”, “What are the likely side effects and who manages them?”, and “What exactly is included in the quoted price?” Proper planning and a clear treatment plan from a trusted team reduce stress and improve the overall patient experience when traveling for CyberKnife.
How to Ensure Safety and Quality of CyberKnife Abroad?
To protect your safety and treatment outcomes when considering CyberKnife abroad, prioritize accredited hospitals, experienced radiation oncology teams, transparent communication, and clear aftercare plans.
Not all clinics are equal. Do thorough vetting before committing—focus on credentials, technology, clinical volume, and how the team manages treatment planning and follow‑up.
- International accreditation: Look for hospitals with Joint Commission International (JCI) or equivalent accreditation as evidence of recognized safety and quality standards.
- Physician credentials and team experience: Verify the radiation oncologist’s board certifications and ask how many CyberKnife cases the team treats annually for your tumor type—team expertise strongly influences outcomes.
- Technology and planning quality: Confirm the clinic uses modern CyberKnife systems, image‑guided planning, and verified motion management to ensure precise dose delivery.
- Transparent communication and documentation: The clinic should provide an itemized quote, a clear treatment plan, expected outcomes, and the radiation dose constraints for nearby organs.
- Aftercare and continuity of care: Ask how follow‑up is managed, whether remote follow‑up is offered, and how the clinic will share reports with your local doctors to ensure coordinated post‑treatment care.
- Patient reviews and outcome data: Request patient testimonials or published outcome data for your tumor type. Real results and complication rates give context beyond marketing claims.
Red flags to watch for
- No clear physician credentials or unwillingness to share team experience.
- Lack of outcome data or only anecdotal testimonials without verifiable references.
- Vague pricing that doesn’t itemize what’s included (planning, imaging, follow‑up).
When in doubt, ask for a second opinion from a local or international radiation oncologist. Good guidance and a qualified team reduce risks and improve the chance that CyberKnife will be an effective treatment for you or your loved one.
What Are Patient Success Stories from Abroad for CyberKnife?
Numerous patients who traveled abroad for CyberKnife report positive outcomes such as good tumor control, limited side effects, and improved quality of life — often paired with satisfaction about the care experience and cost savings from medical tourism.
Below are anonymized case summaries that illustrate how CyberKnife treatment abroad can be applied across different tumor types and patient needs. Note: individual results vary and these examples are illustrative, not guarantees.
- John (Canada) — Prostate cancer: Faced with long local wait times and high costs, John traveled to a JCI‑accredited center abroad for CyberKnife. He completed five high‑dose sessions, experienced only mild urinary irritation, resumed normal activities quickly, and follow‑up imaging showed good local control. He reported significant cost savings compared with domestic private care.
- Maria (UK) — Lung metastasis: After prior treatment, Maria had a small lung metastasis. Offered major surgery at home, she opted for CyberKnife abroad to avoid invasive surgery. The clinic provided a personalized plan, translation support, and outpatient treatment; she had minimal side effects and avoided surgery while maintaining her activity level.
- David (Australia) — Trigeminal neuralgia: Though not a cancer case, David’s severe facial pain was debilitating. He traveled for radiosurgery and found prompt scheduling, experienced gradual pain relief, and praised the professionalism and patient‑centered care he received.
- Sarah (US) — Recurrent brain tumor: With surgery deemed too risky, Sarah sought a CyberKnife center with strong neurosurgical and radiation expertise. Her radiosurgery course reduced tumor size on follow‑up scans, preserved neurological function, and helped her continue rehabilitation at home.
These vignettes highlight potential benefits: targeted tumor control, limited downtime, and, in some cases, lower cost. For balanced decision‑making, ask clinics for anonymized outcome data or published series for your tumor type, and verify that testimonials are supported by clinical follow‑up. If you’d like, request patient references or third‑party outcome reports when evaluating a treatment center — cancer patients planning international CyberKnife treatment should weigh both clinical outcomes and the overall patient experience before deciding.
Take the Next Step with DGS Healthcare
Ready to explore CyberKnife treatment options abroad? Compare vetted clinics, review team experience, and get a free, itemized quote that can include treatment planning, sessions, and pre‑treatment imaging.
Your medical information is used only to provide accurate quotes and clinical assessments — privacy is respected.
